 DRAIPL wins Rail Grinding Machines Contract for Mumbai–Ahmedabad Bullet Train Project
DRAIPL wins Rail Grinding Machines Contract for Mumbai–Ahmedabad Bullet Train Project Four Global Consortia Submit Bids for 65-km Riyadh Metro Line 7
Four Global Consortia Submit Bids for 65-km Riyadh Metro Line 7 Schindler India and Johnson Lifts awarded Escalator and Elevator Contracts for Kochi Metro Phase 2
Schindler India and Johnson Lifts awarded Escalator and Elevator Contracts for Kochi Metro Phase 2 SYSTRA–DB JV bags ₹612 crore Key Systems PMC Contract for Mumbai–Ahmedabad Bullet Train Project
SYSTRA–DB JV bags ₹612 crore Key Systems PMC Contract for Mumbai–Ahmedabad Bullet Train Project Kavach 4.0 covers over 1,300 Route Kilometres across Five Indian Railways Zones
Kavach 4.0 covers over 1,300 Route Kilometres across Five Indian Railways Zones Union Budget 2026 puts India's Rail & Metro sectors on a High-Speed Growth Track
Union Budget 2026 puts India's Rail & Metro sectors on a High-Speed Growth Track AYESA bags First Construction-Linked Tender for Lucknow Metro East–West Corridor
AYESA bags First Construction-Linked Tender for Lucknow Metro East–West Corridor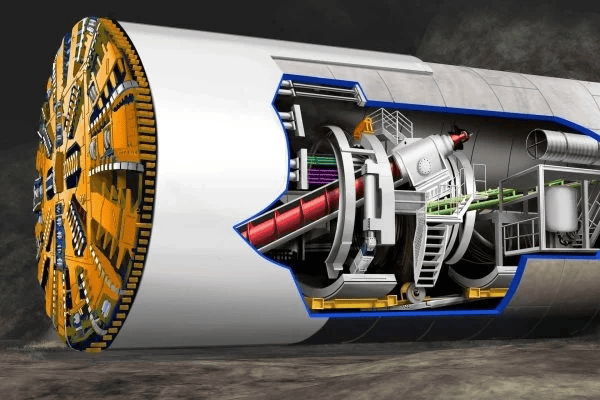 L&T achieves major Tunnel Breakthrough on Delhi Metro Golden Line at IGNOU Station
L&T achieves major Tunnel Breakthrough on Delhi Metro Golden Line at IGNOU Station Rail Chamber submits key recommendations to Railway Ministry for Budget 2026-27
Rail Chamber submits key recommendations to Railway Ministry for Budget 2026-27 Hyderabad Metro at Crossroads: Operational Excellence, Financial Realities and the Future of PPPs
Hyderabad Metro at Crossroads: Operational Excellence, Financial Realities and the Future of PPPs
History of Metro Railways and Subway Systems in the World

Metro rail, also known as a subway, underground, or rapid transit system, refers to an urban passenger transportation system primarily operating on exclusive tracks or tunnels. It typically features electric trains running on fixed routes, offering high-capacity transportation for densely populated areas.
Here are some key characteristics of metro rail/subway systems:
1. Dedicated Infrastructure: Metro rail systems have their exclusive tracks or tunnels, separated from other modes of transportation. This ensures a higher level of reliability, speed, and safety.
2. High Capacity: Metro systems are designed to handle large volumes of passengers efficiently. They often have frequent train services, shorter headways between trains, and the ability to accommodate a significant number of commuters during peak hours.
3. Rapid and Efficient: Metro trains usually operate at high speeds, with limited stops, enabling fast travel times between stations. This makes them an attractive option for daily commuters seeking quick and reliable transportation.
4. Electric Trains: Most metro systems use electric trains that are powered by overhead lines or a third rail. Electric trains offer smoother rides, reduced noise, and lower environmental impact compared to diesel-powered trains.
5. Station Infrastructure: Metro stations are designed with specific features to enhance passenger flow and convenience. These may include multiple entrances/exits, fare collection systems, platform screen doors, elevators, escalators, and signage for easy navigation.
6. Urban Coverage: Metro rail systems primarily serve urban areas, connecting major centers, commercial districts, residential areas, and transportation hubs. They often provide connectivity to key destinations such as airports, train stations, and major tourist attractions.
7. Integration with Other Modes: Metro systems aim to integrate with other modes of transportation, including buses, trams, and bike-sharing services. This seamless integration promotes multimodal travel and provides passengers with convenient options for reaching their final destinations.
8. Safety and Security Measures: Metro systems prioritize passenger safety and security. They typically have surveillance systems, emergency communication systems, well-lit stations, and staff to ensure the well-being of commuters.
The history of metro rail or subway systems dates back to the mid-19th century and has since evolved into an essential mode of urban transport in many cities worldwide. Here's a brief overview of the development of metro rail/subway systems:
1. London Underground, United Kingdom (1863): The London Underground, also known as the Tube, is the oldest metro rail system in the world. It began operations in 1863 with the opening of the Metropolitan Railway, initially using steam locomotives. The system expanded over the years and introduced electric trains in the late 19th century. Today, the London Underground is a comprehensive metro network serving Greater London.
2. Paris Métro, France (1900): The Paris Métro is one of the iconic metro systems worldwide. It opened in 1900, coinciding with the Exposition Universelle (World's Fair) held in Paris. The original line, Line 1, connected important city landmarks, and subsequent lines expanded the network. The Paris Métro is known for its distinctive Art Nouveau entrances and efficient service.
3. Berlin U-Bahn, Germany (1902): The Berlin U-Bahn is a prominent metro system in Berlin, Germany. It opened in 1902 with the initial line connecting several key city points. The Berlin U-Bahn expanded over the years, surviving the division during the Cold War and later integration after the reunification of Germany.
4. New York City Subway, United States (1904): The New York City Subway is one of the most extensive metro systems globally and the oldest in the United States. It opened in 1904 with the Interborough Rapid Transit (IRT) line. Over time, additional lines were constructed, resulting in a vast network that serves the five boroughs of New York City. The subway system played a significant role in shaping the growth and development of the city.
5. Buenos Aires Subte, Argentina (1913): The Buenos Aires Subte is the oldest metro system in Latin America. It began operations in 1913, and the initial line connected Plaza de Mayo to Plaza Miserere. The Subte has expanded since then, serving as a vital mode of transport in Buenos Aires.
6. Madrid Metro, Spain (1919): The Madrid Metro opened in 1919 and has since become one of the largest metro systems in Europe. It has an extensive network of lines serving the city of Madrid and its surrounding areas.
7. Tokyo Metro, Japan (1927): The Tokyo Metro, known as the Tokyo Underground Railway until 2004, is a crucial metro system in Tokyo, Japan. It began operations in 1927, initially with a single line. Over time, the Tokyo Metro expanded with the addition of new lines and extensions, forming an extensive network serving the Greater Tokyo Area.
8. Moscow Metro, Russia (1935): The Moscow Metro, also called the Metropoliten, is renowned for its stunning architecture and grandeur. It opened in 1935 as the first metro system in the Soviet Union. The Moscow Metro expanded rapidly, connecting various parts of the city and serving as a symbol of Soviet engineering and design prowess.
9. Seoul Subway, South Korea (1974): The Seoul Subway system started operating in 1974 and has become an integral part of the transportation network in the South Korean capital. It consists of multiple lines that cover a significant portion of the city and its suburbs.
10. Shanghai Metro, China (1993): The Shanghai Metro began operations in 1993 and has experienced rapid expansion since then. It is one of the largest and fastest-growing metro systems in the world, serving the city of Shanghai and its neighboring regions.
11. Delhi Metro, India (2002): The Delhi Metro started operations in 2002 and has transformed public transportation in the Indian capital. It is known for its modern infrastructure, extensive coverage, and efficient operations.
12. Dubai Metro, United Arab Emirates (2009): The Dubai Metro began operations in 2009 and is the first urban train network in the Arabian Peninsula. It consists of two lines, the Red Line and the Green Line, providing transportation within Dubai and connecting key areas of the city.
13. São Paulo Metro, Brazil (1974): The São Paulo Metro, also known as the Metrô, started operating in 1974 and is an essential mode of transport in the city of São Paulo. It consists of several lines serving the metropolitan area.
14. Vancouver SkyTrain, Canada (1985): The Vancouver SkyTrain is an automated rapid transit system that opened in 1985. It serves the Greater Vancouver region in British Columbia, Canada, with multiple lines connecting the city and its suburbs.
15. Istanbul Metro, Turkey (1989): The Istanbul Metro began operation in 1989 and has expanded considerably since then. It serves Istanbul, the largest city in Turkey, with multiple lines connecting different parts of the city.
These are just a few examples of the early metro rail/subway systems. Since their inception, metro systems have been developed in numerous cities worldwide, each tailored to the specific needs and contexts of the urban areas they serve. Metro rail/subway systems continue to play a crucial role in facilitating urban mobility, reducing traffic congestion, and providing efficient mass transportation options.
These metro rail systems have contributed significantly to the urban transport infrastructure of their respective cities, improving mobility, reducing congestion, and providing efficient transportation options for millions of people.
Metro rail/subway systems play a crucial role in addressing the transportation needs of densely populated urban areas. They offer an efficient, reliable, and sustainable mode of transportation, reducing congestion, air pollution, and travel times. Metro systems are continuously evolving and expanding in cities worldwide to meet the growing demands of urban mobility.






